Ileocolic artery: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
{{dictionary-stub1}} | {{dictionary-stub1}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Gray536.png|Ileocolic artery | |||
File:Gray534.png|Ileocolic artery | |||
File:Gray1043.png|Ileocolic artery | |||
File:Colonic_blood_supply.svg|Ileocolic artery | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 04:57, 18 February 2025
Ileocolic artery
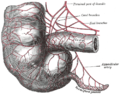
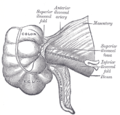
The Ileocolic artery is a branch of the superior mesenteric artery, and supplies the ileum, cecum, and appendix. It is the most distal branch of the superior mesenteric artery.
Anatomy[edit]
The ileocolic artery originates from the superior mesenteric artery, and descends towards the right iliac fossa. It then divides into a superior branch and an inferior branch. The superior branch ascends and anastomoses with the right colic artery, while the inferior branch descends and anastomoses with the superior branch of the inferior mesenteric artery.
Branches[edit]
The ileocolic artery gives off several branches, including:
- Anterior cecal artery and posterior cecal artery: These arteries supply the cecum.
- Ileal arteries: These arteries supply the ileum.
- Appendicular artery: This artery supplies the appendix.
Clinical significance[edit]
The ileocolic artery is susceptible to injury during surgical procedures involving the right lower quadrant of the abdomen, such as appendectomy and right hemicolectomy. Damage to the ileocolic artery can result in ischemia of the ileum, cecum, and appendix, leading to necrosis and peritonitis.