Zinc bis(dimethyldithiocarbamate): Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
{{Chem-stub}} | {{Chem-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
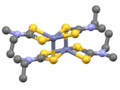
File:Zn(Me2dtc)2dimer.svg|Zinc bis(dimethyldithiocarbamate) dimer structure | |||
File:NAFQUGEtMedtcskewview.png|Zinc bis(dimethyldithiocarbamate) skew view | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 02:12, 18 February 2025
Zinc bis(dimethyldithiocarbamate) (Ziram) is an organosulfur compound with the formula Zn[S2CN(CH3)2]2. It is a coordination complex wherein zinc is coordinated with two dimethyldithiocarbamate ligands. This compound is used primarily in the agricultural industry as a fungicide and in the rubber industry as an accelerator in the vulcanization process.
Properties[edit]
Zinc bis(dimethyldithiocarbamate) appears as a white powder that is insoluble in water but soluble in chloroform and benzene. It decomposes upon heating, emitting toxic fumes of nitrogen oxides, sulfur oxides, and zinc oxide. The compound is known for its fungicidal properties, which make it effective in controlling a variety of plant diseases.
Synthesis[edit]
Zinc bis(dimethyldithiocarbamate) is synthesized through the reaction of dimethyldithiocarbamate sodium salt with zinc sulfate. The process involves the precipitation of the zinc complex from the reaction mixture.
Applications[edit]
Agriculture[edit]
In agriculture, Zinc bis(dimethyldithiocarbamate) is widely used as a fungicide to protect crops against fungal infections. It is effective against a broad spectrum of fungal diseases and is applied to fruits, vegetables, and ornamental plants.
Rubber Industry[edit]
In the rubber industry, it serves as an accelerator in the vulcanization process. It helps in speeding up the cross-linking of rubber, resulting in improved elasticity and strength of the rubber products.
Safety and Environmental Impact[edit]
Zinc bis(dimethyldithiocarbamate) is considered to be of moderate toxicity. It can cause irritation to the skin, eyes, and respiratory system upon exposure. Proper handling and protective equipment are recommended when working with this chemical. Environmental concerns are associated with its use as it can be toxic to aquatic life. Measures should be taken to prevent its release into the environment.
Regulation[edit]
The use of Zinc bis(dimethyldithiocarbamate) in agriculture and other industries is subject to regulation by various international and national agencies to ensure its safe use and to minimize its environmental impact.
See Also[edit]
-
Zinc bis(dimethyldithiocarbamate) dimer structure
-
Zinc bis(dimethyldithiocarbamate) skew view