Coronary sinus: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
{{dictionary-stub1}} | {{dictionary-stub1}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Blausen_0261_CoronaryVessels_Posterior.png|Coronary sinus and vessels, posterior view | |||
File:Gray493.png|Coronary sinus, anatomical illustration | |||
File:Gray491.png|Coronary sinus, detailed anatomy | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 02:11, 18 February 2025
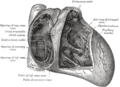
Coronary Sinus
The Coronary sinus is a collection of veins joined together to form a large vessel that collects blood from the myocardium of the heart. It delivers less oxygenated blood to the right atrium, as opposed to the pulmonary veins which deliver oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium.
Structure[edit]
The coronary sinus is located in the coronary sulcus on the posterior side of the heart, between the left atrium and left ventricle. It is directly above the tricuspid valve, which separates the right atrium from the right ventricle.
Function[edit]
The function of the coronary sinus is to collect blood from the veins of the heart and return it to the right atrium. This blood is then pumped to the lungs where it is oxygenated before being returned to the left side of the heart.
Clinical significance[edit]
The coronary sinus can be used in several clinical procedures. For example, it can be used to deliver medication or to perform an angiogram to visualize the coronary veins. It can also be used to implant a pacemaker or defibrillator lead.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />