Costodiaphragmatic recess: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
[[Category:Thoracic cavity]] | [[Category:Thoracic cavity]] | ||
[[Category:Medical terminology]] | [[Category:Medical terminology]] | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Costodiaphragmatic_recess.jpg|Costodiaphragmatic recess | |||
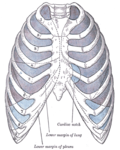
File:Gray965.png|Diagram of the pleural cavities | |||
File:LLL_pneumonia_with_effusionM.jpg|Lower lobe pneumonia with pleural effusion | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 02:10, 18 February 2025
Costodiaphragmatic recess[edit]
The costodiaphragmatic recess is a small anatomical space located between the costal surface of the diaphragm and the lower border of the lung. It is an important area in the thoracic cavity and plays a crucial role in respiration.
Anatomy[edit]
The costodiaphragmatic recess is formed by the meeting of the diaphragm and the lower border of the lung. It is a potential space that is normally filled with a small amount of pleural fluid. The diaphragm is a dome-shaped muscle that separates the thoracic and abdominal cavities, while the lungs are the primary organs of respiration.
Function[edit]
The costodiaphragmatic recess serves several important functions. Firstly, it allows for the movement of the diaphragm during respiration. As the diaphragm contracts and relaxes, it moves up and down, creating changes in the volume of the thoracic cavity. This movement helps in the process of inhalation and exhalation.
Secondly, the costodiaphragmatic recess acts as a buffer zone between the diaphragm and the lower border of the lung. This allows for smooth movement and prevents friction between these structures during respiration.
Clinical Significance[edit]
The costodiaphragmatic recess is an area of clinical importance. It is a common site for the accumulation of pleural fluid, which can occur due to various conditions such as pleural effusion or infection. The presence of excess fluid in the costodiaphragmatic recess can lead to respiratory symptoms such as shortness of breath and chest pain.
In addition, the costodiaphragmatic recess is also a common site for the formation of pleural adhesions. These adhesions can occur as a result of inflammation or injury to the pleural membranes. Pleural adhesions can restrict the movement of the diaphragm and lead to respiratory complications.
References[edit]
<references />
See Also[edit]
-
Costodiaphragmatic recess
-
Diagram of the pleural cavities
-
Lower lobe pneumonia with pleural effusion