Gossypiboma: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
[[Category:Surgical complications]] | [[Category:Surgical complications]] | ||
{{surgery-stub}} | {{surgery-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Gossypiboma_01.jpg | |||
File:Gossypiboma_02.jpg | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 02:04, 17 February 2025
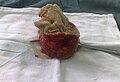
Gossypiboma is a term used in the medical field to describe a retained surgical sponge or towel in a patient's body after undergoing surgery. This condition is a type of surgical complication that can lead to serious health issues, including infection, pain, and obstruction. The word "gossypiboma" is derived from "gossypium" (Latin for cotton) and "boma" (Swahili for place of concealment), highlighting the nature of the condition as a hidden cotton-based material left inside a patient's body.
Causes[edit]
Gossypiboma occurs when surgical sponges or towels, used to absorb blood and fluids or to expose organs during surgery, are inadvertently left inside the patient. This oversight can result from a lapse in the surgical team's counting procedures, miscommunication among staff, or the chaotic nature of emergency surgeries.
Symptoms[edit]
Symptoms of gossypiboma vary depending on the location of the retained sponge and the body's reaction to it. Common symptoms include pain, palpable mass, fever, and infection. In some cases, the sponge may remain asymptomatic and undetected for years.
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis of gossypiboma often involves imaging techniques such as X-ray, CT scan, or Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). These imaging methods can help identify the retained sponge, especially if it contains a radiopaque marker, which is now a standard feature in surgical sponges to prevent such incidents.
Treatment[edit]
Treatment of gossypiboma typically requires surgical removal of the retained sponge. The approach to surgery depends on the sponge's location, the patient's condition, and the presence of any complications such as infection or fistula formation.
Prevention[edit]
Preventing gossypiboma involves strict adherence to surgical counting protocols, use of sponges with radiopaque markers, and employing technological solutions like barcode scanning or radio-frequency identification (RFID) systems to track surgical instruments and sponges.
Legal and Ethical Considerations[edit]
Gossypiboma raises significant legal and ethical issues, including medical negligence, patient safety, and informed consent. Healthcare providers may face legal action from affected patients, leading to compensation claims and damage to professional reputation.