28S ribosomal RNA: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
[[Category:Molecular biology]] | [[Category:Molecular biology]] | ||
[[Category:RNA]] | [[Category:RNA]] | ||
<gallery> | |||
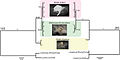
File:16S_and_28S_phylogenies_of_three_Waldo_species_-_ZooKeys-316-067-g003.jpeg|16S and 28S phylogenies of three Waldo species | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 02:04, 17 February 2025
A component of the large subunit of eukaryotic ribosomes
28S ribosomal RNA[edit]
The 28S ribosomal RNA (28S rRNA) is a component of the large subunit (60S) of eukaryotic ribosomes. It plays a crucial role in the process of translation, where it helps in the synthesis of proteins by facilitating the binding of tRNA and the formation of peptide bonds.
Structure and Function[edit]
The 28S rRNA is a large RNA molecule, typically around 4,700 nucleotides in length, although the exact size can vary among different species. It is part of the ribosomal RNA (rRNA) family, which also includes the 5S, 5.8S, and 18S rRNAs in eukaryotes.
The 28S rRNA is involved in the peptidyl transferase activity of the ribosome, which is the enzymatic function that forms peptide bonds between amino acids. This activity is essential for the elongation of the growing polypeptide chain during protein synthesis.
Ribosome Assembly[edit]
In eukaryotic cells, ribosome assembly occurs in the nucleolus, where rRNA is transcribed and combined with ribosomal proteins to form the ribosomal subunits. The 28S rRNA is transcribed as part of a larger precursor rRNA molecule, which also includes the 18S and 5.8S rRNAs. This precursor is processed and cleaved to produce the mature rRNA components.
The 28S rRNA, along with the 5.8S and 5S rRNAs, forms the structural and functional core of the 60S large ribosomal subunit. This subunit then combines with the 40S small subunit, which contains the 18S rRNA, to form the complete 80S ribosome.
Evolutionary Significance[edit]
The 28S rRNA is highly conserved across eukaryotic species, making it a valuable tool for phylogenetic studies. Variations in the sequence of 28S rRNA can provide insights into evolutionary relationships among different organisms. It is often used in conjunction with the 18S rRNA for constructing phylogenetic trees.
Related pages[edit]
Gallery[edit]
-
Phylogenetic analysis using 16S and 28S rRNA
-
16S and 28S phylogenies of three Waldo species