Spirorenone: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
[[Category:Abandoned drugs]] | [[Category:Abandoned drugs]] | ||
{{medicine-stub}} | {{medicine-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Spirorenone.svg|Spirorenone structure | |||
File:Spirorenone_synthesis.svg|Spirorenone synthesis | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:57, 17 February 2025
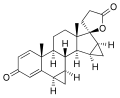
Spirorenone is a steroidal antimineralocorticoid with additional antiandrogen and progestogen properties that was never marketed. It is a spironolactone analogue and was synthesized in the late 1980s as a potential treatment for hypertension and heart failure.
Chemistry[edit]
Spirorenone is a synthetic steroid and is classified as an antimineralocorticoid, or a mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist. It is also considered to be an antiandrogen and a progestogen. The drug is a derivative of spironolactone and is related to other steroidal antimineralocorticoids such as eplerenone and canrenone.
Pharmacology[edit]
The pharmacodynamics of spirorenone involve its action as an antagonist of the mineralocorticoid receptor. This means that it blocks the effects of mineralocorticoids, which are hormones that promote the retention of sodium and the excretion of potassium in the kidneys. By blocking these effects, spirorenone can decrease blood pressure and reduce fluid retention, which can be beneficial in conditions like hypertension and heart failure.
In addition to its antimineralocorticoid activity, spirorenone also has antiandrogenic and progestogenic properties. This means that it can block the effects of androgens, or male sex hormones, and can mimic the effects of progesterone, a female sex hormone. These properties could potentially make spirorenone useful in the treatment of conditions like androgen-dependent diseases and menstrual disorders, although the drug was never marketed for these uses.
History[edit]
Spirorenone was synthesized in the late 1980s as a potential treatment for hypertension and heart failure. However, it was never marketed, possibly due to the development of other, more effective antimineralocorticoids like eplerenone.
See also[edit]
-
Spirorenone structure
-
Spirorenone synthesis