Spiroxasone: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|A synthetic steroidal antimineralocorticoid and antiandrogen}} | |||
{{Drugbox | |||
| verifiedfields = changed | |||
| verifiedrevid = 477002123 | |||
| image = Spiroxasone.png | |||
| image_size = 200px | |||
| image_alt = Chemical structure of Spiroxasone | |||
}} | |||
'''Spiroxasone''' is a synthetic [[steroidal antimineralocorticoid]] and [[antiandrogen]] that was developed for the treatment of conditions such as [[hypertension]] and [[heart failure]]. It is a derivative of [[spironolactone]], a well-known [[potassium-sparing diuretic]]. | |||
==Pharmacology== | |||
== | ===Mechanism of Action=== | ||
Spiroxasone acts as an antagonist of the [[mineralocorticoid receptor]], which is responsible for the effects of [[aldosterone]] in the body. By blocking this receptor, spiroxasone reduces sodium reabsorption and increases potassium retention, leading to a diuretic effect. Additionally, it has antiandrogenic properties, which means it can block the effects of [[androgens]] like [[testosterone]]. | |||
===Pharmacokinetics=== | |||
The pharmacokinetic profile of spiroxasone includes its absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion. Like other steroidal antimineralocorticoids, it is metabolized in the liver and excreted primarily in the urine. | |||
== | ==Clinical Use== | ||
Spiroxasone was investigated for use in conditions such as [[hypertension]], [[heart failure]], and [[hirsutism]]. However, it was never marketed, and its clinical use remains limited to research settings. | |||
==Side Effects== | |||
Potential side effects of spiroxasone include [[hyperkalemia]], [[gynecomastia]], and [[menstrual irregularities]]. These are similar to those observed with other antimineralocorticoids and antiandrogens. | |||
== | ==Chemical Structure== | ||
[[File:Spiroxasone.png|thumb|right|Chemical structure of Spiroxasone]] | |||
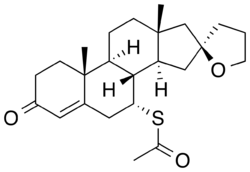
Spiroxasone is a synthetic steroid with a chemical structure similar to that of spironolactone. It contains a lactone ring and a thioacetate group, which are characteristic of this class of compounds. | |||
==Related Compounds== | |||
Spiroxasone is related to other antimineralocorticoids such as [[spironolactone]] and [[eplerenone]]. These compounds share similar mechanisms of action and therapeutic uses. | |||
== | ==Related pages== | ||
* [[Spironolactone]] | |||
* [[Eplerenone]] | |||
* [[Mineralocorticoid receptor]] | |||
* [[Antiandrogen]] | |||
[[Category:Antimineralocorticoids]] | |||
[[Category:Antiandrogens]] | |||
[[Category:Synthetic steroids]] | |||
[[Category: | |||
[[Category: | |||
[[Category: | |||
Latest revision as of 04:02, 13 February 2025
A synthetic steroidal antimineralocorticoid and antiandrogen
| Spiroxasone | |
|---|---|
| |
| INN | |
| Drug class | |
| Routes of administration | |
| Pregnancy category | |
| Bioavailability | |
| Metabolism | |
| Elimination half-life | |
| Excretion | |
| Legal status | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
Spiroxasone is a synthetic steroidal antimineralocorticoid and antiandrogen that was developed for the treatment of conditions such as hypertension and heart failure. It is a derivative of spironolactone, a well-known potassium-sparing diuretic.
Pharmacology[edit]
Mechanism of Action[edit]
Spiroxasone acts as an antagonist of the mineralocorticoid receptor, which is responsible for the effects of aldosterone in the body. By blocking this receptor, spiroxasone reduces sodium reabsorption and increases potassium retention, leading to a diuretic effect. Additionally, it has antiandrogenic properties, which means it can block the effects of androgens like testosterone.
Pharmacokinetics[edit]
The pharmacokinetic profile of spiroxasone includes its absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion. Like other steroidal antimineralocorticoids, it is metabolized in the liver and excreted primarily in the urine.
Clinical Use[edit]
Spiroxasone was investigated for use in conditions such as hypertension, heart failure, and hirsutism. However, it was never marketed, and its clinical use remains limited to research settings.
Side Effects[edit]
Potential side effects of spiroxasone include hyperkalemia, gynecomastia, and menstrual irregularities. These are similar to those observed with other antimineralocorticoids and antiandrogens.
Chemical Structure[edit]

Spiroxasone is a synthetic steroid with a chemical structure similar to that of spironolactone. It contains a lactone ring and a thioacetate group, which are characteristic of this class of compounds.
Related Compounds[edit]
Spiroxasone is related to other antimineralocorticoids such as spironolactone and eplerenone. These compounds share similar mechanisms of action and therapeutic uses.